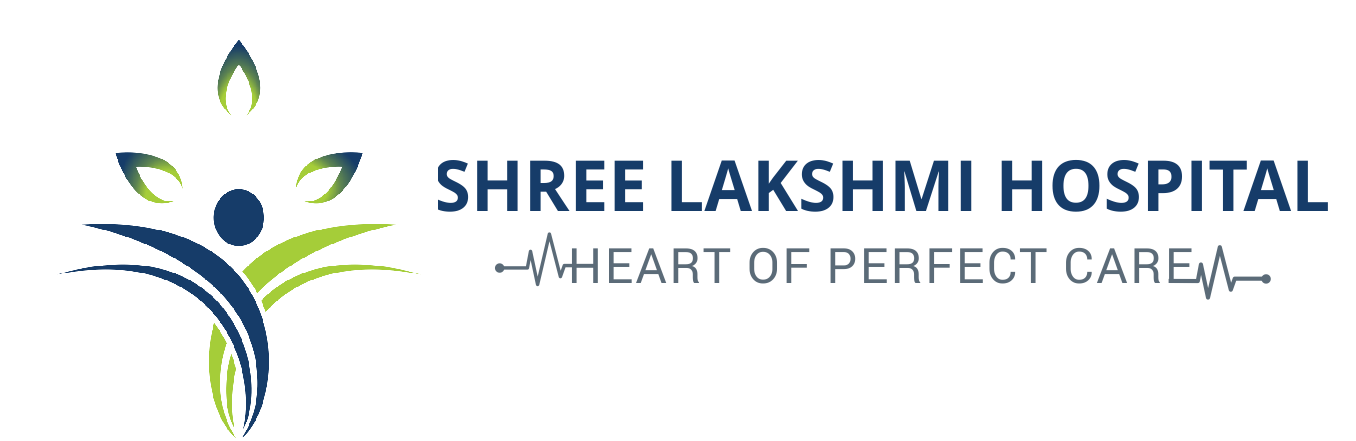Infertility happens when a couple cannot conceive after having regular unprotected sex.The cause of infertility may be difficult to determine but may include inadequate levels of certain hormones in both men and women, and trouble with ovulation in women.
There are two types of infertility, primary and secondary.
Primary infertility : It refers to couples who have not become pregnant after at least 1 year having sex without using birth control methods.
Secondary infertility: It refers to couples who have been able to get pregnant at least once, but now are unable.
Many physical and emotional factors can cause infertility. It may be due to problems in the woman, man, or both.
FEMALE INFERTILITY
Female infertility may occur when:
- A fertilized egg or embryo does not survive once it attaches to the lining of the womb (uterus).
- The fertilized egg does not attach to the lining of the uterus.
- The eggs cannot move from the ovaries to the womb.
- The ovaries have problems producing eggs.
- Female infertility may be caused by:
- Autoimmune disorders, such as antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
- Birth defects that affect the reproductive tract
- Cancer or tumor
- Clotting disorders
- Diabetes
- Drinking too much alcohol
- Exercising too much
- Eating disorders or poor nutrition
- Growths (such as fibroids or polyps) in the uterus and cervix.
- Medicines such as chemotherapy drugs
- Hormone imbalances
- Obesity
- Older age
- Ovarian cysts and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Pelvic infection resulting in scarring or swelling of fallopian tubes (hydrosalpinx) or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Scarring from sexually transmitted infection, abdominal surgery or endometriosis - Smoking
- Surgery to prevent pregnancy (tubal ligation) or failure of tubal ligation reversal (reanastomosis)
- Thyroid diseases
MALE INFERTILITY
Male infertility may be due to:
- Decreased number of sperm
- Blockage that prevents the sperm from being released
- Defects in the sperm
- Male infertility can be caused by:
- Birth defects
- Cancer treatments, including chemotherapy and radiation
- Exposure to high heat for prolonged periods
- Heavy use of alcohol, marijuana, or cocaine
- Hormone imbalance
- Impotence
- Infection
- Medicines such as cimetidine, spironolactone, and nitrofurantoin
- Obesity
- Older age
- Retrograde ejaculation
- Smoking
- Toxins in the environment
- Vasectomy or failure of vasectomy reversal
Healthy couples under age 30 who have sex regularly will have a 25% to 30% per month chance of getting pregnant each month.
Natural cycle monitoring, counselling about fertile period
2. Ovulation induction with tablets and follicular monitoring
3. Superovulation with injectables (Gonadotrophins), follicular monitoring and luteal support.
4. SPERM Quality and Quantity are improved by traditional ways, tablets, hormonalinjections.
5. Erection and ejaculation or semen collection issues are addressed
6. Intra Uterine Insemination (IUI)
7. Myomectomy, septal resection, vaginoplasty
8. Endometriotic cystectomy
9. Tubal recanalization
10. In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
11. Green IVF or minimal stimulation protocol
12. Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
13. MESA, TESA, TESE
14. Donor Oocyte program
15. Surrogacy
16. Donor Embryo Program
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) :
At the time of ovulation, a fine catheter is inserted through the cervix into the uterus to place a sperm sample directly into the uterus. The sperm is washed in a fluid and the best specimens are selected.
IUI is more commonly done when the man has a low sperm count, decreased sperm motility, or when infertility does not have an identifiable cause. It can also help if a man has severe erectile dysfunction.
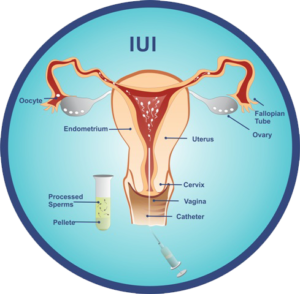
In-vitro fertilization (IVF) :
Sperm are placed with unfertilized eggs in a petri dish, where fertilization can take place. The embryo is then placed in the uterus to begin a pregnancy. Sometimes the embryo is frozen for future use.
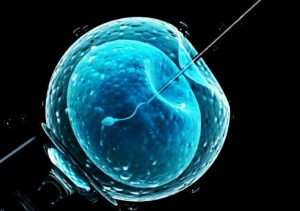
IVF Process :
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) :
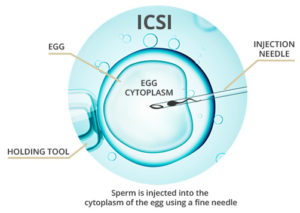
A single sperm is injected into an egg to achieve fertilization during an IVF procedure. The likelihood of fertilization improves significantly for men with low sperm concentrations.
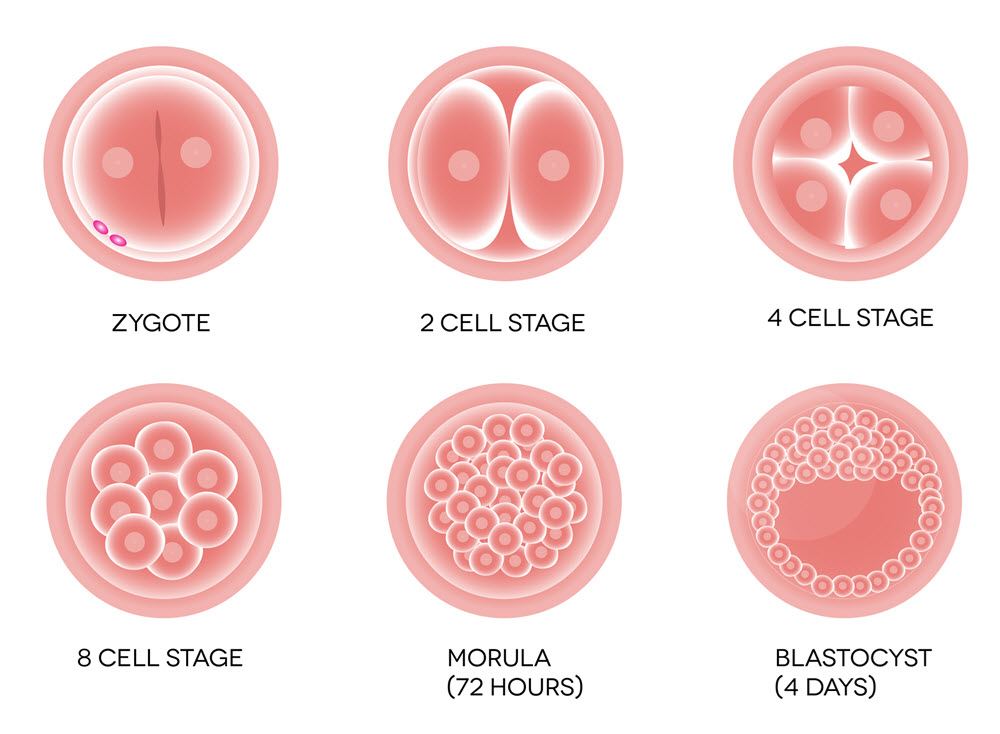
Embryo Development:
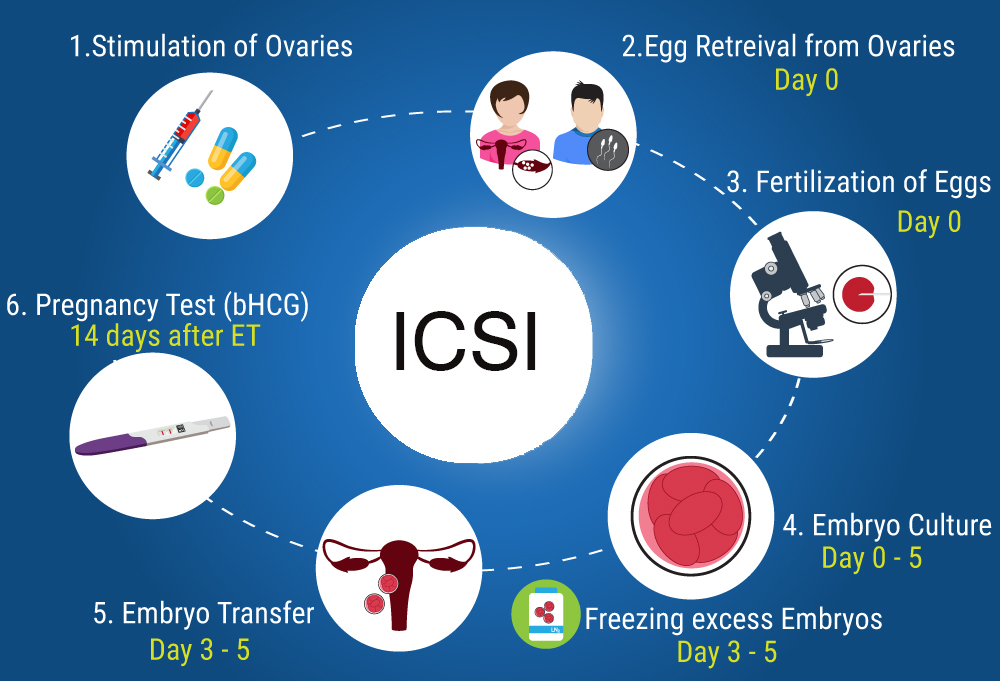
ICSI Procss :
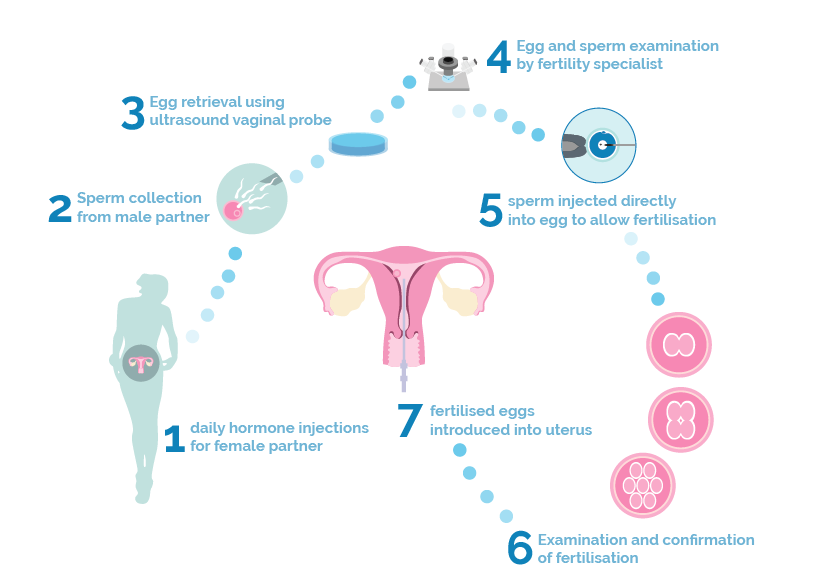
Sperm or egg donation:
Sperm or eggs can be received from a donor. Fertility treatment with donor eggs is usually done using IVF.
Surgical sperm aspiration:
The sperm is removed from part of the male reproductive tract, such as the vas deferens, testicle, or epididymis.